Class 11 biology chapter - 1- the living world notes
 |
| The living world |
Life is a characteristic quality that differentiates inanimate (non-living)objects from the animate (living) forms.
 |
| Characteristics of living beings |
Biodiversity
It is the degree of variability among living organisms. It includes all the varieties of plants and animals. It encompasses all the ecological complexes (in which the diversity occurs), ecosystem, community diversity, species diversity and genetic diversity. It comprises all the millions of species and the genetic differences between them.
Systematics
It is the study of the biodiversity. It attempts to classify the diversity of organisms on the basis of following four fields viz, identification, classification, nomenclature.
1. Identification
It aims to identify the correct name and position of an organism in the already established classification system. It is done with the help of keys. Key is a list of alternate characters found in organisms. An organism can be identified easily by selecting and eliminating the characters present in the key.
2. Classification
It involves the scientific grouping of identified organisms into convenient categories or taxa based on some easily observable and fundamental characters. The various categories which show hierarchical arrangement in decreasing order are Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
3. Nomenclature
After classification, organisms are subjected to a format of two-word naming system called binomial nomenclature. It consists of two components, i.e., generic name and specific epithet. For example, in Mangifera indica, ‘Mangifera’ is the generic name and ‘indica’ is the specific name of mango. This system was proposed by C Linnaeus (a Swedish Botanist) in (1753) in his book Species Plantarum. Polynomial system of nomenclature is a type of naming system containing more than two words. Trinomial system is a component of polynomial system and contains three words. Third word represents the sub-species and first two-words remain the same as in binomial system.
Codes of Biological Nomenclature
There are five codes of nomenclature which help to avoid errors, duplication and ambiguity in scientific names. These codes are as follows
ICBN International Code of Botanical Nomenclature
ICZN International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
ICVN International Code of Viral Nomenclature
ICNB International Code for Nomenclature of Bacteria
ICNCP International Code for Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants
Taxonomy
It deals with the principles and procedures of identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms. It reflects the natural and phylogenetic relationships among organisms. It also provides the details of external and internal structures, cellular structure and ecological information of organisms. The term taxonomy was coined by AP de Candolle, 1813.
Various Branches of Taxonomy
Alpha (α) Taxonomy Morphological traits
Artificial Taxonomy Habit and habitat of organisms
Natural Taxonomy Natural similarities among organisms
Chemotaxonomy Presence or absence of chemicals in cells or tissues
Cytotaxonomy Cytological studies
Numerical or Phenetic Taxonomy Number of shared characters of various organisms
Phylogenetic or Omega (ω) Taxonomy Based on phylogenetic relationships
Classical Taxonomy
It is also known as old taxonomy. In classical taxonomy, species is the basic unit and it can be described on the basis of one or few preserved specimens. Organisms are classified on the basis of some limited features.
Modern Taxonomy/New Systematics
The concept of modern taxonomy was given by Julian Huxley (1940).According to it, species are dynamic and ever-changing entity. Studies of organisms are done on a huge number of variations. It includes cytotaxonomy, numerical taxonomy, chemotaxonomy, etc.
Taxonomic Categories
Classification is not a single step process. It involves hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category. Since, the category is a part of overall taxonomic arrangement, it is called the taxonomic category. The taxonomic categories, which are always used in hierarchical classification of organisms are called obligate categories. The sub-categories like sub-species, sub-class, sub-family, etc., which facilitate more sound and scientific placement of various taxa are called intermediate categories. Arrangement of taxonomic categories in a descending order during the classification of an organism is called taxonomic hierarchy. It was first introduced by Linnaeus (1751) and hence, it is also known as Linnaean Hierarchy.
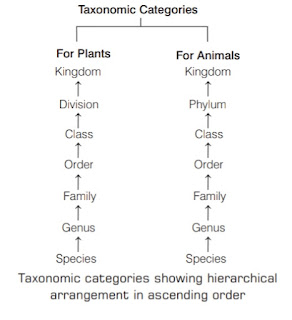 |
| Taxonomic categories |
Taxonomical Aids
They include techniques, procedures and stored information that are useful in identification and classification of organisms. Some of the taxonomical aids are as follows.
Importance of Taxonomical Aids
● These aids help to store and preserve the information as well as the specimens. The collection of actual specimens of plant and animal species is essential and is the prime source of taxonomic studies.
● These are also essential for training in systematics which is used for the classification of an organism. Hence, taxonomic aids facilitate identification, naming and classification of organisms using actual specimens collected from the fields and preserved as referrals in the form of herbaria, museums, etc.
FAQs
the living world class 11 notes,
The living world,
The living world class 11,
class 11 biology chapter 1 the living world notes,
